Nvidia’s Jensen Huang has created much buzz around AI and robotics in his keynote speech this month at the CES 2025. When it comes to robots, they are certainly not new to manufacturers who have been deploying industrial robots for years to increase productivity at their facilities.
However, humanizing robots and developing humanoids is a trickier process way behind industrial robots in the commercial curve. With that said, the rapid ascent of AI technology has convinced many that the age of advanced robotics has arrived where AI acts as an accelerator to bring use cases of robotics and automation from industrial applications to households and consumers.
While consumer products may be some way from now, industrial applications of automation robots harnessing AI technology can possibly materialise in the not-so-distant future. Many countries are at the forefront of this technology, from Japan to Europe and China.
Across the supply chain, there are various products and parts such as the sensors, motors and drives, controls and the software layer. Japan remains one of the more mature economies for the use of robots, with cutting edge vision-guided robotics still nascent but possessing vast potential for widespread adoption.

More broadly, machine vision and AI work hand-in-hand to contribute to the growth of robots and automation. At the highest level, autonomous robots can help to replace both low-value and high-value labor, freeing up valuable resources to handle other demanding aspects of the value chain that is harder to automate.
To be sure, this shift towards more advanced robotics will be one of a gradual process if we recall the commercialisation path for industrial automation some 30 to 40 years ago. From there, what becomes more certain is the customer confidence and multi-year penetration of the technology once the initial barrier to adoption has been overcome.
An evidence of this evolution can be found in the rising share of collaborative robots in the large manufacturing market of China. According to varying sources, collaborative robots as a share of robot shipments into China climbed steadily for the past 5 years, alongside a productivity drive and a push to lower the reliance of a labor force (which can be vulnerable to disruption from pandemics lockdowns or movement control orders). This trend also took roots owing to the fact that the Chinese market is often more open and receptive to experimenting with newer technologies, due to the intense competition and room for risk-taking in the manufacturing industries.
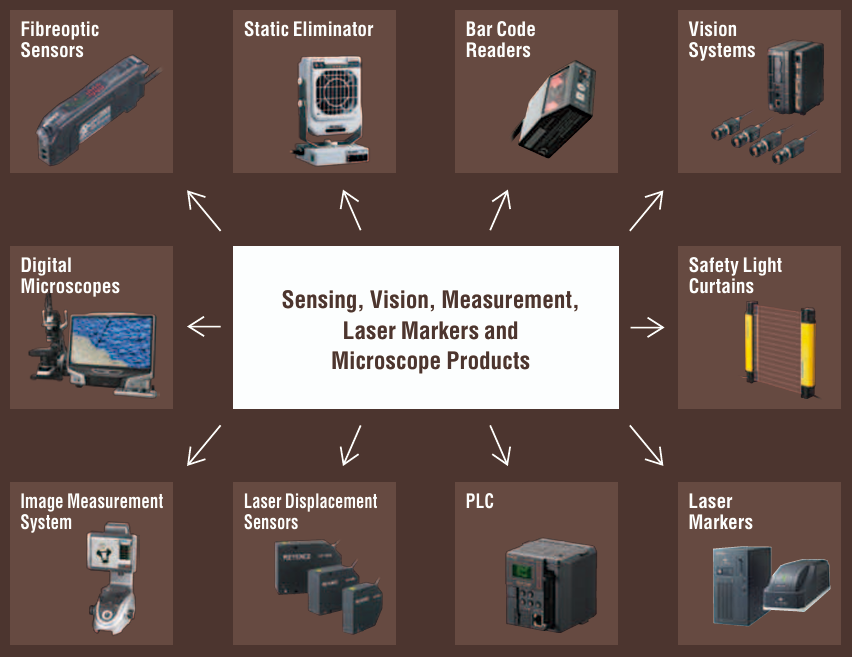
Focusing on Keyence itself, there have been doubts of whether the company can maintain its market leadership in the face of rising competition both locally and globally from countries where cost of production is lower. However, there are two main competitive moats which contribute to the defensiveness of their business.
Keyence’s products are an enabler to machine vision, and its hardware specifications set the playing field for which other AI software companies can build upon. This positions Keyence to be one of the most direct beneficiary of industrial automation and AI-power robotics. The company’s innovation also compounds into a durable form of R&D excellence; allowing them to continually offer new products to their customers across a wide range of applications and cementing their market leadership in the domain of sensors and vision specialty.
Another key differentiating element for Keyence business model is that they do not strive to compete in highly-customised orders, but instead seek to leverage its broad technology know-how to deploy solutions at scale to many of its customers. What the company has shown is that the enduring dominance of its hardware and design capabilities allows it to maintain an ecosystem for which their customers have to operate within. Other third party providers may be able to compete on pricing, but less likely to be able to do so at Keyence's technical capabilities across multiple deployments.
When it comes to comparison with other industrial giants like Siemens and Omron (where they have a much more diversified portfolio of products and solutions), Keyence manages to carve out a niche in 3D vision guided robotics due to their historical specialisation. This form of technology gives rise to better autonomous path planning, an essential foundation for robots to operate in dynamic scenarios. The amount of data they measured and gathered will allow AI to be deployed more efficiently, vastly improving the adaptive aspect of the robots.
The realm of humanoids is an exploding field of interest which captures the imagination of many. The system complexity increases substantially from here, and two countries, United States and China, jostle for intellectual property prowess in this arena. To date, key technical challenges and critical hurdles to overcome still exist in humanoid development.
That said, AI advancements will likely accelerate the movement planning and reactive coordination elements of humanoids. For instance, Google DeepMind utilises reinforced learning AI technique as an approach for the humanoid to identify ways to complete tasks instead of programming exact locomotion to navigate specific determined environments in real life. Plugging into where Keyence comes to play, in terms of AI vision, they are necessary for the sensing and perceiving functions of the real-world environment as well as creating a simulated digital replica of it.
We are indeed at an interesting juncture where the current AI investment momentum provides the necessary boost towards greater capital formation in the industry. Aside from many less-proven AI applications for enterprises and consumers in the making, what may end up proving AI investments to be effective may well be in the relatively duller space of advanced industrial automation and humanoids.